·
A sub-region refers to a small area within a
region.
·
Due to various factors, the people of a
sub-region feel that they possess a distinct
identity.
·
A
movement for the separation of that sub-region from a state or for the
redressal of grievances in the sub-region is known as sub-regionalism.
Sub Regionalism
in HP
1.
Old Himachal v/s New Himachal
2.
Upper Himachal v/s Lower Himachal
3.
Cap Politics
4.
Cultural Divide
1. Old
Himachal v/s New Himachal
1.1 OLD HIMACHAL- SHIMLA HILLS
- In Himachal Pradesh present day
consist of two types of hills areas.
- Before independence, the first type
of areas was ruled by native princes.
- In these areas the people struggle was influenced by
nationalist movement in British India, but its object was never to overthrown or
totally eliminates their princely states.
- Most
of these areas were of Old Himachal and popularly known as Shimla Hills.
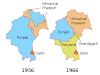
1.2 NEW
HIACHAL- PUNJAB HILLS
·
The other hill areas which joined Himachal
Pradesh in 1966 were under direct British administrative control before
independence.
·
The people in these areas participated in the struggle for freedom with the specific objective of
overthrowing alien British rule.
·
These areas were known as Punjab Hills.
·
Thus in hilly region prior to independence, two types of
movements were going on simultaneously i.e.
a)
The
Prajamandal Movement in
Princely States.
b)
The
Freedom Movement in
Punjab Hill States.
2. UPPER
VS LOWER HIMACHAL
2.1 Upper
Himachal
·
Shimla
Region,
which includes the districts of Shimla, Sirmaur and Solan.
2.2 Lower
Himachal
·
Kangra
region
comprising of the districts of Kangra, Hamirpur and Una.
·
Whereas Shimla region is a part of the 'old'
areas, Kangra region constitute the
part of 'New' areas which were merged with Himachal Pradesh on November 1st, 1966, as a result of the bifurcation of Punjab on linguistic basis.
·
Ever since the
merger of hilly areas of Punjab with Himachal Pradesh, the State has been
facing an 'integration crisis' in the form of sub-regional conflict between the
'Old' and the 'New' areas which has surfaced in successive
elections' to the State Assembly since 1966.
·
Congress
government main leader and former six time chief minister Virbhadra
Singh has dominance in Shimla Hill
region while BJP has dominance in lower foothills as seen in election results
also.
·
As BJP CM candidate belong from lower Himachal and Congress candidates came from Upper Himachal
·
With this sub
regionalism in state priorities given to some areas and others left are ignored for the sake of
regional political gains.
3. CAP POLITICS
- The
electorate in Himachal Pradesh wears the loyalties
not on their sleeves but on their heads.
- In this hilly state, they
pronounce their loyalty and support
through their headgear.
- If cap is in maroon front the
person belong from Bhartiya Janta
Party( BJP) supporter and if green the
person is with congress.
- The concepts of green and maroon
stem from upper and lower areas of the state.
- It started with six time congress chief minister Virbhadra
Singh who loves to don a green flap headgear almost throughout
the year. His supporters to prefer to wear this colour of cap to
express political solidarity with him.
- Likewise BJP leader and two time
chief minister Prem Kumar Dhumal has made the maroon flap
his trademark.
4.
CULTURAL DIVIDE.
- There is a large cultural divide in Himachal Pradesh
on the basis of language, religion,
folk songs, dances etc.
- In some areas of Upper Himachal
Peoples mainly in kinnaur high hills, Lahaul spiti follow Bodh religion due to contouring Tibetan boundaries while in lower Himachal
Hinduism, Islam is the main religion.
- Dance, dresses, songs can also be
compared in these areas.
- Nati is the favourite dance in high hills while in lower hills
which is bit aligned to Punjabi culture Gidha, Bhangra is most
prevalent in these areas.
- Also same is with cuisine Siddu is served in High hills while in lower areas Makki ki roti and sarson ka saag is served in winter mainly
which is also famous in Punjab.
- All
these factors are not much important to peoples, they all live with unity but these
cultural disparities are used for political advantages to gain votes, divide
people on their political ideology for their party benefits and people get
influenced by them and within region, in one state people seen divided.
- If this thing keeps on feeding
people, then some areas which are not much developed can demand separate
administration which will cost government in many ways.
Reasons & outcomes of
sub-regionalism
- Sub-regionalism
is closely
connected to the economic structure particularly
to the processes of modernization.
- Sub-regionalism is a phenomenon
that manifests
itself at the political level using cultural distinctiveness and economic
discrimination as supporting factors.
- Political
parties & consequently governance are influenced by regionalism.
- This is manifested by domination
of either of the major parties in each region.
- A perceptual divide happens due to regional emotions.
Case
Study:
- The dormant regional sentiments
came to surface during the agitation
(July-August 1990) spearheaded
by the vegetable and fruit growers of Shimla region against the anti-growers
policy of the newly elected State government headed by Shanta Kumar.
- The
agitation which began with certain
economic demands like support
price for the various cash crops, took the regional dimension when people of Kangra origin residing
in the apple belt became the target of the agitators.
- Some
shops belonging to the people of Kangra were reported to be looted or
burnt.
- Some of them had to leave the region out of the fear for their life.
- Though
the state
government with the help of police force curbed the agitation,
it has already done irreparable
damage to the emotional integration in the state.
- Now the sub-regionalism had become an established fact of State politics
which is slowly dissolving away.








0 Comments